The Residents Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) encompasses 150 megahertz of spectrum within the 3.5 GHz band (3550 MHz–3700 MHz), with plans to increase by an extra 100 megahertz. Traditionally, this spectrum has been actively utilized by the U.S. authorities and the Coast Guard. Since 2020, the Federal Communications Fee (FCC) has categorized CBRS as an “unlicensed spectrum” for shared wi-fi personal broadband.
The FCC established two tiers for spectrum entry: Normal Licensed Entry (GAA) and Precedence Entry Licenses (PAL). The GAA tier supplies “free” spectrum allocation of 80 MHz inside the 150 MHz band, whereas the PAL tier consists of licensed spectrum segments acquired by way of public sale. PAL licenses, which include 10-MHz unpaired channels inside the 3.55-3.65 GHz vary, are dynamically assigned by the Spectrum Entry System (SAS) and are issued on a county-level foundation for a 10-year time period. Throughout the public sale, roughly 20,625 licenses have been bought, producing income exceeding $4.5 billion.
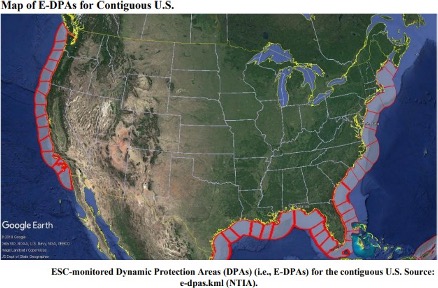
Nevertheless, this funding is accompanied by important regulatory constraints. In areas designated for army operations, Dynamic Safety Areas (DPAs) have been established to safeguard incumbent radar methods. Inside these DPAs, CBRS operations over specified frequency ranges are prohibited each time radar methods are lively. Every DPA is outlined by a frequency vary the place radar operations might happen, and all factors inside the DPA have to be protected against interference, whether or not by co-channel or out-of-band (OOB) CBRS emissions.
One of many main challenges for service suppliers is the restriction on CBRS operations in massive incumbent-protected areas. When incumbent transmissions begin, CBRS service in these areas should stop, creating important protection gaps and operational limitations for service suppliers.
Determine 1: Dynamic Safety Areas (DPAs) within the continental U.S.
Within the CBRS 1.0 framework, the heartbeat interval and transmit expiry timer posed important challenges for service suppliers. The CBSD (Residents Broadband Service Gadget) periodically sends a heartbeat request to the SAS (Spectrum Entry System), usually at intervals of 5 minutes or longer, to take care of its spectrum grant. In response, the SAS supplies a heartbeat response, which incorporates the transmit expiry time — the time at which the CBSD should stop transmissions if no additional authorization is acquired, plus a 60-second grace interval. If the CBSD fails to obtain a response or re-synchronize with the SAS earlier than the timer expires, it should cease transmitting, leading to a service outage. This course of, crucial for spectrum administration, typically created disruptions, particularly in circumstances of community instability or latency, resulting in interruptions in CBSD operations till the SAS hyperlink was re-established.
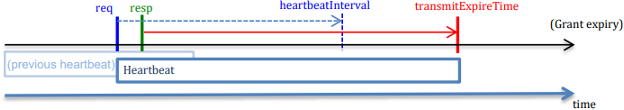
The brief period of the “transmit expiry timer” has been a major concern, as it will possibly result in service outages. If the timer expires and the CBSD (Residents Broadband Service Gadget) fails to re-synchronize with the SAS (Spectrum Entry System) server, the CBSD will stop operation and stay offline till the CBSD-SAS hyperlink is re-established.
One other crucial situation is interference. As CBRS operates as an “unlicensed spectrum,” a number of CBSDs typically transmit concurrently in shut proximity, resulting in potential interference. To mitigate this, methods such because the unicast topology have been carried out, whereby all CBSDs transmit uplink and downlink concurrently utilizing TDD (Time Division Duplex) to forestall cross-link interference. Whereas the PAL spectrum is safeguarded by way of designated PAL Safety Areas (PPAs), the GAA spectrum stays unprotected besides by way of controls carried out by the SAS server or mechanisms just like the “GAA-Coexistence” group.
The FCC has addressed these challenges in its newest tips, as outlined in a number of public notices.
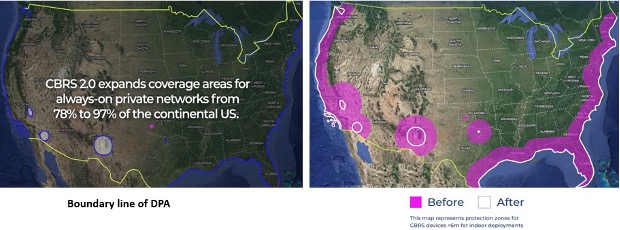
The redesign of Dynamic Safety Areas has considerably diminished their measurement in comparison with the unique CBRS 1.0 framework. This discount ensures that CBRS operations can increase whereas persevering with to guard army methods. Smaller safety zones imply extra areas are actually out there for CBRS operations. Gadgets that beforehand skilled interruptions as a consequence of incumbent actions can now function with out the chance of preemption, guaranteeing constant connectivity. For indoor deployments beneath 6 meters, the proportion of the inhabitants outdoors safety zones is projected to extend from 49% to 91%.
By efficiently implementing these adjustments, SAS directors are anticipated to authorize service for about 72 million further folks, bringing the entire nationwide protection to an estimated 240 million.
Determine 2: Comparability of DPA zones for CBSD below 6 meters for indoor deployments earlier than (purple) and after (white) the implementation of recent tips or CBRS 2.0.
The opposite situation of Heartbeat interval together with transmit expiry timer is relaxed now. As per the brand new NTIA tips, “lengthening this reauthorization interval from 5 minutes to 24 hours which are outdoors of the scope of present federal operations will assist to supply a extra secure and predictable spectrum setting for all CBSD units of any class (Cat-A/Cat-B).
Determine 3: Comparability of CBSD periodic timer earlier than & after the implementation of recent guidelines or CBRS 2.0.
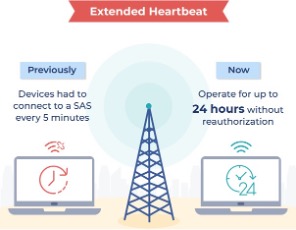
Although it’s strongly advisable to not use a 24-hour lengthy wait interval, as an alternative most OEM prefers as much as six hours at most with out the necessity to reauthorize from SAS server. Additionally, the “transmit expiry timer” may be set to a most of 24 hours for the complete band outdoors DPA zones and inside the higher
50 MHz spectrum vary. The profit from this method in mitigating the potential for service disruptions, guaranteeing much more constant and dependable connectivity for CBRS customers specifically for Mission crucial use circumstances.
The final one is Interference administration for GAA CBSD units. As per the brand new tips, an non-obligatory coexistence mechanism is proposed to be carried out inside SAS to assist in imposing frequency planning and interference restrictions throughout CBSDs in coordination with GAA operators. There’s already a Collaborative GAA Coexistence framework outlined in On-Go Alliance which included the next occasions:
- Interference Detection and Validation
- Creation of GAA Coordination Space
- GAA Frequency Plan and GAA Frequency Plan Negotiation
- Implementation of the GAA-negotiated frequency Plan
The newly added procedures for SAS server in CBRS 2.0 are the next:
- The SAS directors might assume an 80% TDD exercise issue and 20% community loading issue for every CBSD within the combination interference calculation. The overall impression will scale back, by 8 dB, the equal EIRP used within the combination interference calculations for every CBSD by SAS.
- The SAS directors might use median Irregular Terrain Mannequin (ITM) terrain-dependent propagation loss (in dB) — utilizing reliability and confidence elements of 0.5 — to calculate the combination acquired energy ranges inside a DPA which was beforehand 0.95.
- The SAS directors might apply median litter loss — calculated utilizing the methodology described in Advice ITU-R P.2108,9 part 3.2 — for any CBSD with an antenna top Above Floor Degree (AGL) of lower than or equal to 6 meters, that’s working at a distance of a minimum of 250 meters from a DPA boundary.
Conclusion — How will these adjustments rework present CBRS deployments?
The brand new tips maintain important promise to boost capability, protection and total consumer expertise. The discount in DPA sizes is anticipated to considerably enhance spectrum availability, significantly in coastal areas, main to raised protection and capability for operators. Enhanced interference mitigation, by way of a coordinated coexistence mechanism amongst GAA CBSDs, is poised to ship a smoother and extra dependable end-user expertise. Moreover, this enchancment might be amplified if OEMs implement key modifications in 5G-DU (Layer 2 MAC) and 5G-NRT-RIC, enabling environment friendly administration of intra-PLMN CBSDs for optimized interference dealing with. Collectively, these developments place CBRS 2.0 as a pivotal step ahead in delivering high-quality, reliable connectivity.

